Concentrol is a chemical solutions company with the objective of providing references to streamline the production processes of professionals working in various sectors.
The release agents offered by Concentrol have been developed after years of research and experience acquired in sectors such as automobiles, footwear, furniture, construction and others.
Molded polyurethane parts are essential in the vast majority of the sectors mentioned above, and their use is constantly expanding. These components play a fundamental role in the production of advanced polymeric materials. The different applications can be grouped according to the type of foam and the type of process, giving rise to the following divisions: hot curing flexible foam ; cold curing flexible foam ; flexible, rigid and semi-rigid integral skin foam ; rigid, semi-rigid and RIM foam; and elastomers.
In the next Research Blog we will explain what rigid polyurethane foam release agents are and what characteristics they have, focusing especially on two key sectors: insulation and automobiles.
Release agents for rigid foam: What are they for?
Polyurethane rigid foam release agents are chemical agents designed to facilitate the release process during the manufacture of rigid foams . Known for their exceptional insulating properties, these foams are used in a wide range of applications, from construction to the manufacturing of components for the automotive industry.
In the insulation sector , where energy efficiency and sustainability are essential, rigid foam release agents play a crucial role. They facilitate the smooth and precise demolding of polyurethane foams, allowing the creation of highly efficient insulating products. From panels to thermal insulation systems, these release agents contribute to the creation of more energy efficient structures, improving quality of life and reducing the environmental footprint.
In the automotive sector , where the constant search for lighter and stronger components is a priority, rigid foam release agents also play an essential role. By facilitating the production of structural and insulating parts, these compounds contribute to the creation of more efficient vehicles in terms of weight and performance. From seats to interior panels, the application of mold releases in the manufacturing of automotive components drives innovation and sustainability in the industry.
Types of release agents for rigid polyurethane
Rigid polyurethane is a material with a great function as a thermal insulator . Its low thermal conductivity is due to its closed cellular structure, a characteristic that allows energy savings through thermal insulation. There are different release agents for rigid polyurethane, which are:
- Solvent-based release agent for rigid polyurethane
- Water-based release agent for rigid polyurethane
- Concentrated water-based release agent for rigid polyurethane to dilute
- Release agent for rigid polyurethane based on concentrated solvent to dilute
- Solvent-based paste release agent for rigid polyurethane
The parts obtained by demolding with rigid foam are mainly insulating panels of continuous and discontinuous production, as well as insulation parts for automobiles and external decorative parts such as spoilers. Other imitation wood pieces can also be created for decoration or furniture.
The molds that give rise to these pieces can be made of aluminum, wood, stainless steel or epoxy resin . In foam demolding facilities, for sectors such as automotive or furniture, steel and/or aluminum molds are usually used, while in countries or sectors with limited technology or with more relaxed acceptance and quality standards, materials such as epoxy resin can be used. and wood. It is important to keep in mind that, in the production of demolded rigid foam with a water-based or hybrid product, if the solution comes into contact with ferrous surfaces, signs of oxidation may appear in the short or medium term.
Industrial facilities using rigid foam
Installations that use this type of foam are usually carousels for small parts, static molds or slabstock -type continuous production systems .
Insulation sandwich panels:
Sandwich panels are made up of an insulating core of rigid polyurethane or polyisocyanurate foam (PUR-PIR) adhered to two faces that are usually metal, and the metal layers are generally made of steel or aluminum.
During the manufacturing process, the cover layers are prepared by profiling them according to the desired initial shape. Once shaped as required by each type of panel, they are transported to the press, and there the mixing head injects the necessary components with a predetermined dosage, forming the foam in the liquid phase. Its chemical reaction causes the foam to grow, adhering to the two layers of coverage, the bottom and the top. By applying heat and pressure for a certain time until curing, we obtain what is known as dimensional stability of the core.
The release agent is previously applied to the sides of the press , where there will be direct contact between the rigid foam and the mold.
Applications of PUR/PIR sandwich panels:
The field of application of PUR-PIR sandwich panels is very similar, since it can be applied to facades, roofs, false ceilings, interior partitions and cold rooms. Specifically, they serve to:
- Thermal insulation for the construction of refrigerated trucks.
- Thermal insulation of floors in cold rooms and freezing tunnels.
- Thermal insulation in sandwich panels with metal sheet, polyester, wood, fiber cement, etc.
- Working temperature range: temperatures below 0°C up to 80°C.
- Support for pipes and pumps, machined in the form of half shells.
- Industrial warehouses, airports, administration buildings, booths and prefabricated houses, hotels, exhibition halls and fairgrounds, laboratories, clean rooms and operating rooms, paint rooms, power plants, recycling plants and waste incineration plants, sports centers, large stores commercial, roofs and facades of homes, conservation rooms, process rooms, etc.
Advantages and disadvantages of using rigid foam
With the use of rigid foam, pieces with a dry finish and a surface that can range from closed to completely open pores are obtained. The final piece can also have different densities, depending on the customer’s purpose and process.
The main benefits of using rigid foam are:
- Acoustic absorption properties : Helps put an end to annoying noises both outside and inside. Polyurethane is an excellent acoustic insulator.
- Moisture elimination : With rigid polyurethane, continuous insulation is achieved in the area to be rehabilitated. Thanks to its waterproof characteristics, polyurethane foam is able to prevent moisture from entering and, at the same time, allows breathing on a microscopic scale, preventing the accumulation of microorganisms and fungi.
- Sealing layer : Polyurethane creates a sealing layer that prevents cracks and possible air or water leaks.
- Thermal performance and cellular structure: With polyurethane, maximum insulation is obtained with minimum thickness , thanks to its thermal performance and cellular structure.
The use of rigid foam also poses a series of difficulties :
- Mold temperatures can be very low.
- Large pieces or pieces with cavities that are rigid to remove.
- The subsequent cleaning and painting process should not be excessively affected by the release agent, or it may even be necessary that the demolded parts can be painted without degreasing. In some cases it is necessary to work with silicone-free release agents to avoid their non-adhesion and contaminating effect, since a small amount is enough to cause painting problems, wetting defects and holding the paint on the surface. There are several procedures to ensure painting and high adhesion, but in this sector the most common thing is that mechanical polishing is carried out before painting.
Application systems
The application systems will depend on the type of products used:
- Products that can be classified as class 1 , that is, ready to use and with a flash point below 21°C, can be applied without problems with air-less equipment, since they do not need the help of air to dry the film on the surface. mold.
- Class 2 products dry more slowly and, therefore, it is advisable and essential to use drying equipment for 1 to 1.5 minutes, with the mold between 50 and 70 °C.
The sizes of the filters to be used are determined by the size of the pieces to be removed from the mold and by the time available to apply the release agent to all corners of the mold. Generally, we can talk about sizes of 0.5 mm for standard parts, and 1.2 to 1.5 for large parts.
Regarding the use of airbrush or air-mix equipment, it should be said that airbrush equipment is comfortable to use, especially the Shütze brand guns, which are small in size and light in weight. These have product pressure and air pressure, with which the spraying is regulated.
Air -mix are more effective in robotic release agent application, where more possibilities of movements and shapes of the fan are needed to reach the entire mold, without complex path programming. These have more than one additional air outlet, which helps regulate the three-dimensional shape of the fan up to conical-shaped spraying.
The air-less applicator only has one air pressure to propel the product, and with the help of the shape and dimensions of the filter, it is necessary to find the fan that is best. It does not help drying at all, so it is not useful in many applications.
Cleaning the molds
After removing the pieces from the mold, other processes will be carried out such as painting, with which the piece is usually polished to eliminate any previous residue of the release agent.
The cleaning of the molds will depend on the residue left in the mold after the work cycles, varying depending on the type of polyurethane pieces being modeled, PUR system and type of release agent. However, it is important to keep in mind that the interaction with the components is always present, whether to a greater or lesser degree.
Only the release agents that leave a soft residue can be cleaned with liquid products , and the others, as can be seen in the following diagram, allow variations according to each chain and client.
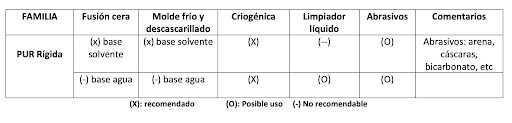
Wax Melting: The wax is melted on the mold by temperature and more infrared light is applied as reinforcement or a blower. Once it is melted, remove it with a clean cloth, repeating if necessary.
Cold and chipped mold: The mold is allowed to cool to room temperature. Since the wax is hard, it tends to break up with the help of a scraper, and the entire layer can be removed.
Cryogenic: The mold is impregnated with dry gel as an abrasive, obtaining a new mold. Before foaming, it is necessary to apply several layers of release agent or reinforcing paste. This system is especially necessary with water-based release agents, since together with the remains of wax and the active substance of the release agent, polyureas accumulate resulting from the interaction of remains of non-evaporated water with the isocyanate, which leads to a material infusible. The cryogenic system is based on the projection of dry ice (carbon dioxide) on the surface of the molds using high-pressure compressed air. The projection of these pellets, which could also be walnut shells or other similar pellets, causes a thermal contrast that, together with the impact of the projection, causes the residue on the surface to jump. After impact, these dry ice pellets sublime into a gaseous state and, together with the air current caused, convert dirt into macroparticles.
Cleaner: Only for soft residues such as waxes, resins, oils or silicones, among others.
Abrasives: It is a system similar to cryogenic, although less aggressive. In this case, instead of dry ice, sand, nut shells or baking soda, among others, are used.
The best Concentrol references
The CONCENTROL® range provides specific and efficient solutions for all types of polyurethane panels, including those increasingly demanding in terms of surface finish, high productivity, cost, mold cleanliness, easy application and protection of the environment. work and the environment.
The range of products is very wide, with solvent-based and water-based mold release agents, concentrates and dilutable concentrates. In addition, customized solutions can be designed according to the client’s needs.
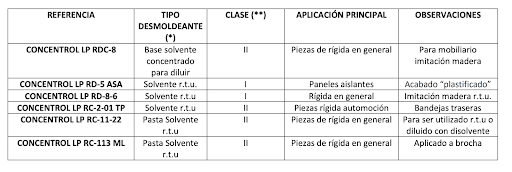
Below is a table with the name of the reference and its main characteristics, as well as the application:
New developments
Concentrol’s R&D department is studying launching two new products on the market, which are:
- CONCENTROL LX RP-3-01: High performance release paste. It is a paste product, ready to use or to be diluted with aliphatic hydrocarbons from 1:1 to 1:4. The finish of the piece is slightly greasy and has excellent release capacity, even in difficult areas. It is applied by brush or broom, and with a single application it can provide 3 to 6 releases.
- CONCENTROL LP PFA-132 V: Water-based paste for rigid in general. It can be used at a working temperature between 45 and 65 °C. Application is by brush and serves as a reinforcement for water-based release agents in difficult areas.
Complementary additive products
Concentrol also offers a series of additive references that can be complementary to these processes, which are:
- CTDC ADDITIVE: Foam hardener that improves mold release.
- ESFCJ ADDITIVE: Foam surface film former that helps close pores and prevents surface collapses.
- ADDITIVE-14: Less active foam surface film former that provides a certain lubricating effect to the piece when unmolding it.
- NK ADDITIVE: Water-based foam hardener to improve mold release.
- ADDITIVE NK-2: DBTDL-free, water-based foam hardener to improve mold release.
- ESFW ADDITIVE: Surface film former for water-based foam that closes pores and prevents surface collapses.
Concentrol can supply products to all sectors with traditional solvent-based release agents, concentrates, dilute concentrates, hybrids and water-based. Concentrol’s range of release agents is very wide and is constantly developing, which keeps us at the forefront of the current challenges set by the industrial sector.
After more than 75 years of work in the sector, at Concentrol we have the goal of innovating with chemistry to have a positive impact on society and the planet. As leaders in the chemical solutions sector, we play a fundamental role in the evolution and continuous improvement of industrial processes. Join us on this journey towards innovation and sustainability!


